Overview of Override Rules
Override rules allow you to supersede the default processes by which Time Management determines (derives) who approves particular time sheet lines and which charge codes apply to those lines.
For information about specifying a resource's default time approvers, see Configure time sheet policy and approvers. For information about how Time Management derives approvers, including the priority of override rules, see Determine time approvers.
For information about configuring charge codes and how Time Management prioritizes override rules in determining them, see Charge codes.
All override rules have the following two parts:
-
Dependencies. The filters that must be satisfied to apply the override rule.
-
Results. The resulting rules that apply when the specified dependencies are met.
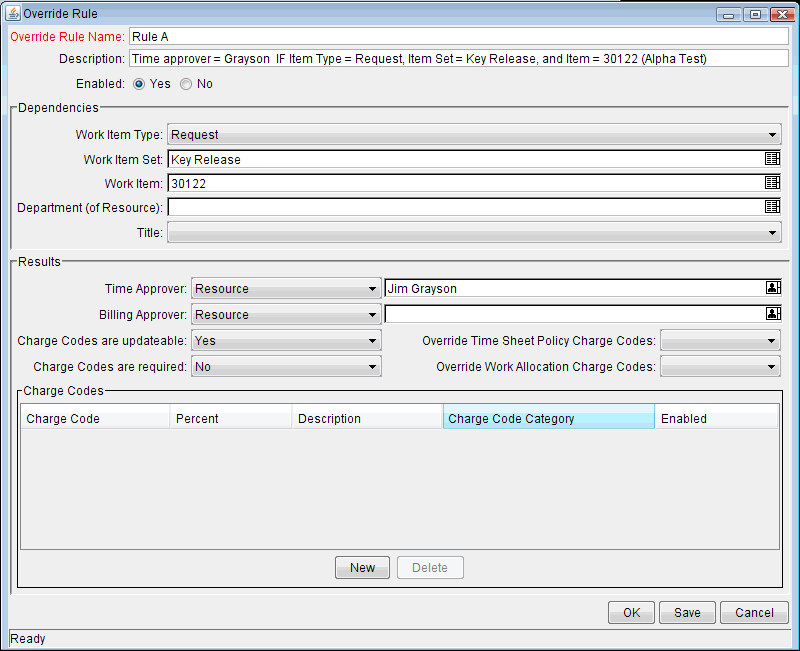
Figure 7-1. Example Override Rule window shows an example of an override rule with Dependencies and Results sections. The Work Item Type, Work Item Set, and Work Item dependencies are related to the time sheet line and the Department (of Resource) and Title dependencies are related to the resource. You can specify all or any subset of the five dependencies in an override rule. If all the specified dependencies are met, then the specified rules in the Results section are applied to the associated time sheet line.
If dependencies for more than one override rule are met, only the override rule with the highest precedence takes effect. See Precedence of Dependencies Among Multiple Override Rules for detailed information about override rule precedence.
If results of an override rule are not specified, other override rules with lower precedence can provide results under some circumstances. See Precedence of Results Between Override Rules and Other Settings.
When the dependencies of an override rule are met, the various results of the override rule are applied at specific times of the Time Management process, as indicated in Table 7-1. When rules are applied.